CURABITUR ALIQUET QUAM POSUERE
Welcome Aboard Us!
Subscribe to our emails for the latest industry updates and special offers.
Will be used in accordance with our Privay Policy

The heat exchangers commonly used in the chemical industry have the following classification methods:
1) Classified by heat transfer mode. Mixed heat exchanger, regenerative heat exchanger, interwall heat exchanger.
2) Classification by structure. Tube heat exchanger, plate heat exchanger, heat exchanger form.
3) Classification by use. Heater, preheater, superheater, evaporator, reboiler, cooler, condenser.
4) Sort by material. Metallic materials, non-metallic materials.
5) According to the shape and structure of the heat transfer surface classification. Fixed tube-plate heat exchanger, U-tube heat exchanger, stuffing box heat exchanger, kettle heat exchanger.
Usually in daily work is mainly classified according to the structure, the following is a comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of several commonly used heat exchangers:
1, fixed tube-plate heat exchanger:
(1) The heat transfer area is large, about 20-30%; No internal leakage, less forging, low cost;
2, floating head heat exchanger:
(1) can be extracted, easy to clean, medium temperature difference is not limited;
(2) A section is not connected to the object, and when the pipe is heated, the bundle together with the floating head can be freely expanded along the axis.
(3) Two tube plates, easy to occur internal leakage, large metal supplies, high cost, complex structure.
(4) The heat transfer effect is better than that of U-tube heat exchanger.
3, U-tube heat exchanger:
(1) can be drawn out, easy to clean, not limited by temperature difference;
(2) The pipe path is not suitable for medium with large structure.
(3) Simple structure, only one tube plate.
(4)Suitable for scenarios where the heat transfer efficiency is not particularly high and the budget is limited.
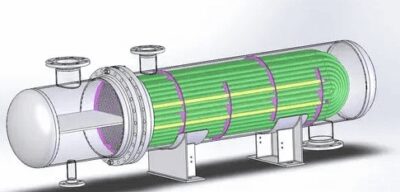

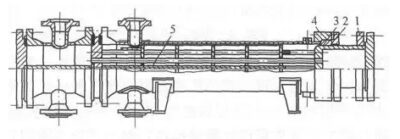
4, stuffing box heat exchanger
(1) The bundle can be freely telescopic, and there is no temperature difference stress between the bundle and the shell.
(2) Simple structure, convenient manufacture, easy maintenance and cleaning.
(3) There is the possibility of external leakage of shell fluid, so the use of pressure and temperature are limited.
(4) The shell should not be volatile, flammable, explosive and toxic media.

5, plate heat exchanger
(1) Large heat exchange area, less consumables, small size, small footprint.
(2) Easy to disassemble and clean.
(3) Price comparison economy.
(4) poor sealing, easy to leak, often change the washer.
(5) Poor pressure effect, easy to plug. Not suitable for gas heat transfer or steam condensation.

